Curriculum
The subjects studied by pupils make up the curriculum. The school will deliver the curriculum in 5 lessons of 60 minutes each per day over a period of 10 days.
Years 7 - 9
All pupils will study the same subjects for the first three years at West Park School.
- Mathematics
- English - Language and Literature
- Science - Biology, Chemistry and Physics
- Technology - Electronics, Food, Graphics, Resistant Materials and Textiles
- Art
- Humanities - Geography, History and Religious Studies
- Music
- Drama
- French
- Physical Education
- Information and Communication Technology
- Personal Development - (including Personal, Social and Health Education and Careers)
Years 10 - 11
- All pupils will take English Language, Literature, Mathematics, Core and Additional Science, (5 or 10 periods), Geography or History, ICT and Religious Studies at examination level. PE (2 periods) and Careers (1 period) are compulsory but not examined.
- About 50% will also take French which, in addition to the core subjects, will make up the EBacc suite of subjects. All pupils can follow the EBacc suite of subjects if the other 50% choose to take French, but it is not compulsory for these pupils.
- Pupils not chosen to take French will take PE (GCSE or Btec) in addition to the core of subjects.
- EBacc pupils can opt to take PE at examination level.
- Approximately 5% will take GCSE Core and Additional Science (5 periods). This is a bespoke course designed for pupils for whom 5 periods of science rather than 10 will provide them with a better balanced curriculum.
- Pupils sit an entrance examination to gauge their suitability for taking the triple Science course.
- 95% of pupils can choose one subject and 5% two subjects, in addition to their core of subjects.
- Additional subjects are chosen from:
- GCSE courses in: Art, Drama, French, Geography, History, Music, Physical Education, Technology (Electronics, Food, Graphics, Resistant Materials or Textiles).
- BTEC courses in: Creative Digital Media Production
- Additional information about the curriculum offered can be obtained by contacting the relevant head of department.
For more information regarding the curriculum, please contact neil.allsop@westpark.derby.sch.uk.
Maths Curriculum
Mathematics is a creative and highly inter-connected discipline that has been developed over centuries, providing the solution to some of history’s most intriguing problems. It is essential to everyday life, critical to science, technology and engineering, and necessary for financial literacy and most forms of employment. A high-quality mathematics education therefore provides a foundation for understanding the world, the ability to reason mathematically, an appreciation of the beauty and power of mathematics, and a sense of enjoyment and curiosity about the subject.
The aims of the Mathematics Department at West Park School mirror those of the National Curriculum to ensure that all pupils:
- Become fluent in the fundamentals of mathematics, including through varied and frequent practice with increasingly complex problems over time, so that pupils develop conceptual understanding and the ability to recall and apply knowledge rapidly and accurately.
- Reason mathematically by following a line of enquiry, conjecturing relationships and generalisations, and developing an argument, justification or proof using mathematical language.
- Can solve problems by applying their mathematics to a variety of routine and nonroutine problems with increasing sophistication, including breaking down problems into a series of simpler steps and persevering in seeking solutions.
Mathematics is an interconnected subject in which pupils need to be able to move fluently between representations of mathematical ideas. The key stages of study are, by necessity, organised into apparently distinct domains, but pupils should make rich connections across mathematical ideas to develop fluency, mathematical reasoning and competence in solving increasingly sophisticated problems. They should also apply their mathematical knowledge to Science and other subjects. The majority of pupils will move through the programmes of study at broadly the same pace. However, decisions about when to progress will always be based on the security of pupils’ understanding and their readiness to progress to the next stage. Pupils who grasp concepts rapidly are challenged through being offered rich and sophisticated problems before any acceleration through new content. Those who are not sufficiently fluent with earlier material will consolidate their understanding, including through additional practice, before moving on.
The Mathematics curriculum at West Park School is accessible to all pupils and allows them to reach their full potential. This is done through consistently good and outstanding teaching which instills in pupils an enjoyment of Mathematics and encourages them to become independent learners.
Pupils have a positive experience studying Mathematics. Teachers are highly skilled subject specialists who use a variety of mastery methods to promote deep mathematical understanding. Pupils strive to improve their knowledge and are encouraged to become motivated independent learners.
The programme of study for Key Stage 3 is organised into apparently distinct domains, with pupils building on Key Stage 2 and connections across mathematical ideas to develop fluency, mathematical reasoning and competence in solving increasingly sophisticated problems.
The programme of study for Key Stage 4 is again organised into apparently distinct domains, but pupils develop and consolidate connections across mathematical ideas. Pupils build on learning from Key Stage 3 to further develop fluency, mathematical reasoning and competence in solving increasingly sophisticated problems.
The Mathematics curriculum is written to provide a smooth progression through Years 7 to 11. The schemes of work cover all of the mathematical content in the 9-1 GCSE and are differentiated according to the ability of the pupils with pupils being set accordingly. Sets are frequently reviewed. The schemes of work for Year 7 and Year 8 have recently been re-written by the Maths leadership team to adopt the philosophy of mastery learning more strongly. This is an ongoing process working towards embedding deeper knowledge and skills. At the end of Year 11 pupils sit the Edexcel GCSE Mathematics examinations, this is offered at Higher and Foundation tier.
English Curriculum
Our curriculum has been designed to ensure that our pupils have a depth of knowledge, enjoy their learning and understand the significance that English (both Language and Literature) has in the wider world. We are passionate about our pupils seeing the world through the lens of Literature, and we know it is vital that West Park pupils leave fully equipped as literate members of society who are able to express themselves confidently. We also hope they will develop a lifelong love of reading.
Year 7
- Heroes and Villains – pupils will explore a series of famous literary characters understanding what creates a hero and a villain. Pupils will experience examples from: fiction, non-fiction, from famous myths and legends, short extracts and full novels. The knowledge built here of literary concepts underpins the analysis of texts explored throughout their time at West Park.
- Viewpoint and Perspectives – through our topic on the theme of ‘Adventures and Experiences’, pupils will consider how writers present their viewpoints and ideas about the world. Pupils will engage with non-fiction writing from a range of time periods exploring how writers present their narratives about the world as they see it.
- Ghost Stories – Pupils will prepare for their examination style assessment in a unit focusing on supernatural stories. In this topic, pupils are introduced to the concept of the Gothic, exploring and introducing the conventions used in this genre.
- Poetry – pupils are introduced to a range of poetry building a foundation for the skills of literary analysis moving forward. We will consider a varied and engaging selection of poems and begin to develop their confidence in exploring writers’ ideas and the language and structure choices used in poetry.
- History of Literature – our pupils are taken on a journey through time, considering key pieces of Literature that have influenced writers and still resonate with the world we live in today. From Beowulf to Shakespeare to more contemporary writing, pupils are encouraged to understand the journey our language has taken over time and the ‘literary influencers’ that have shaped modern writers’ ideas and styles.
Year 8
- Gothic Literature – Pupils develop their knowledge and understanding of Gothic writing through time, building a confident understanding of the conventions used in this genre. They will draw on their Year 7 knowledge and dig deeper into the ideas and themes explored by writers of the Gothic. Pupils will experience classic gothic writing – with extracts from Frankenstein and Dracula and also more modern gothic stories from some of the most popular writers of teenage fiction today.
- The Gothic Play – Pupils apply their knowledge of the gothic, studying a playscript version of a classic text and explore how gothic elements are presented in different forms of fiction.
- Overcoming Challenges – building on their knowledge of non-fiction from Year 7, pupils will develop their understanding of how non-fiction writing can give a voice to those in challenging situations or with important viewpoints to share. This helps to enable them form their own opinions and voices as they begin to articulate their own ideas and express their interpretations of attitudes and perspectives.
- Short Stories – pupils will study examination skills through a range of modern stories. We begin to focus on structural elements considering how these, along with the language chosen, can impact the development and style of a story.
- Romeo and Juliet – after being introduced to Shakespeare in Year 7, pupils now consider this classic play in greater depth, building on their growing knowledge of language, structure and themes to explore this text.
Year 9
- Exploring Modern Stories – in this unit, pupils develop their understanding of story construction, structure features and language through the exploration of a range of modern, thought-provoking texts.
- Voices of Change – pupils build on the skills introduced in years 7 and 8 to understand how non-fiction writing has been used throughout history to give people from different backgrounds a voice to change society. Pupils will explore complex concepts and varied methods to reflect upon texts about key events in society, showing them the transformative power of words and writing.
- ‘Macbeth’ – pupils are introduced to this Shakespearean classic to establish an understanding of plot, central characters and key themes. This first study gives pupils a fundamental comprehension of the play which underpins the teaching of the whole text undertaken in Year 10.
- Exploring Genres – pupils use their knowledge of genre from the Gothic Literature scheme in Year 8 to understand the different conventions of a range of genres from Literature though time. We encourage pupils to experiment with writing from these genres and to be daring with their own writing, building creative, original pieces of prose.
- Bonnie and Clyde and Relationships Poetry – pupils will read a non-fiction text exploring the modern classic tale of Bonnie and Clyde. This study enables pupils to explore themes that are revisited in the GCSE texts. As this story has a love story at its cores, we couple this with an introduction to some of the love poetry from the ‘Love & Relationships’ GCSE cluster.
Year 10
- Creative Reading and Writing – pupils are introduced to the first full English Language paper applying examination skills to engaging fiction stories. This culminates in a ‘walkthrough’ assessment, a supported first attempt at a Paper 1 examination. This scaffolded approach helps to build confidence and guide pupils in this early introduction to the first GCSE paper.
- The Sign of the Four – pupils study a Victorian Sherlock Holmes novel understanding how this famous sleuth impacted the detective genre. Pupils study the text in detail considering plot, structure, the methods used and how it fits into its historical and literary context.
- Viewpoints and Perspectives – pupils will apply all of their non-fiction learning to complete an English Language Paper 2. Again, this will be supported through a ‘walkthrough’ approach to continue to build confidence and develop examination technique.
- Macbeth – pupils will study the play in full building on their prior knowledge from Year 9. Pupils develop further their understanding of plot, characters, themes and Shakespeare’s’ use of language in this core GCSE text.
- Love and Relationships Poetry and Unseen Poetry – Pupils will study the Love and Relationships poetry throughout the year, studying a pair of linked poems each half term. They will also continue to analyse unseen poems, securing their understanding of poets’ ideas and messages and developing their use of poetic terms in poetry analysis.
Year 11
- An Inspector Calls – pupils consider social and political issues and a number of complex concepts through the study of this modern playscript. Pupils consider how literature can be used to question political thinking, present philosophical messages about society and bring about social change.
- Revision Programme – in preparation for the GCSE examinations, pupils re-visit all Literature texts and Language examination papers once again focussing an all of the assessment objectives examined by AQA. The programme is carefully planned so that all pupils experience a rich revision programme and are prepared to face the final examinations with the skills and confidence they need to secure GCSE success.
The Wider Curriculum - we offer a range of extra opportunities including:
We encourage all of our pupils to read widely around topics we study in class. All units of learning are accompanied by a wider reading list available for pupils to seek out more knowledge, context or to offer alternative ideas about each area of study.
Our book club is very successful and popular in school, and we constantly take every opportunity to encourage a culture of reading, questioning and wider enrichment.
We also undertake period 6 sessions to support and mentor students who may need extra support or challenge.
We offer theatre experiences with visits from drama groups and through streamed performances.
We arrange visits from published authors who share their experiences of writing with the pupils – these take varying forms - small group sessions, opportunities for pupils to interview our guests’ authors or through talks to larger groups.
Science Curriculum
Year 7
- Cells and Movement - Plant and animal cells, specialised cells, the muscular and skeletal systems and the organisation of living things.
- Human Reproduction and Variation - The male and female reproductive systems, sex cells and their functions, sexual intercourse, gestation, birth, menstruation and variety in characteristics.
- Interdependence and Plant Reproduction - Habitats, how different species depend upon each other, food chains and webs, plant reproductive systems.
- Particle Theory and Separating Mixtures - Solids, liquids and gases, changes of state, diffusion, air pressure, Brownian motion, distillation, filtration, evaporation, chromatography.
- Acids and Alkalis and Metals and Non-Metals - Everyday acids and alkalis, hazards, the pH scale, neutralisation, metal salts, properties of metals and non-metals.
- The Earth and The Universe - The structure of the Earth, resources from the Earth, climate change, the Earth in space, seasons, planets, day and night, constellations, geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar system.
- Speed and Gravity - Calculating speed, distance-time graphs, speed-time graphs, gravity and weight.
- Sound and Light - The mechanism by which sound travels, speed of sound and light, refraction, reflection and dispersion.
- Voltage and Resistance and Current - Building simple circuits, measuring voltage and current, series and parallel circuits, calculating resistance and models of circuits.
- Energy Costs and Energy Transfers - Electricity bills, types of energy, energy stores, energy transfers and alternative methods of generating electricity.
Year 8
- Breathing and Digestion - The respiratory system, the mechanics of breathing, the digestive system, nutrition and food tests.
- Inheritance and Evolution - Inherited characteristics and diseases, DNA, extraction of DNA, the process of evolution, evidence for evolution.
- Respiration and Photosynthesis - The equation for respiration, the products of respiration, exercise, the equation for photosynthesis, products of photosynthesis, factors affecting photosynthesis.
- The Periodic Table and Elements - The structure and organisation of the periodic table, groups of the periodic table, metals and non-metals, patterns of reactivity, elements and compounds.
- Chemical Energy and Types of Reaction - Fuels and combustion, chemical and physical changes, observing reactions and recording observations, the fire triangle, exothermic and endothermic reactions.
- Climate and Products from the Earth - Pollution, composition of the atmosphere, alternative methods of metal extraction, products from the land, sea and air, rocks and the rock cycle.
- Contact Forces and Pressure - Friction, balanced and unbalanced forces, moments, levers, force diagrams, pressure calculations.
- Wave Effects and Wave Properties - Types of wave - longitudinal and transverse, wave properties and characteristics, electromagnetic waves.
- Electromagnets and magnetism - Magnetic materials, permanent and induced magnets, making an electromagnet, factors affecting the strength of an electromagnet.
- Work done and heating and cooling - Calculating work done, calculating energy transfers, convection, conduction and radiation.
Year 9
- Cells - Plant, animal, bacterial and yeast cells, specialisation and differentiation of cells, microscopy, chromosomes, mitosis and the cell cycle, stem cells.
- Disease - Communicable and non-communicable diseases, viral, bacterial, fungal and protest disease, human defence systems, vaccination, antibiotics and painkillers and the discovery and development of drugs.
- Ecology Part 1 - Adaptions, independence and competition, abiotic factors, biotic factors, organisation in an ecosystem.
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table - The development of the periodic table, the modern periodic table, the atom, the history of the structure of the atom, electronic structure, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases.
- Chemical changes - The reactivity series of metals, reactions of acids, metal salts, neutralisation reactions, the pH scale, strong and weak acids.
- Radioactivity - The development of atomic theory, types of radiation, radioactive decay, decay equations, half-life, radioactive hazards and contamination, irradiation.
- Energy - Energy transfers, energy stores, conservation of energy, potential and kinetic energy, power, work done, alternative sources of energy.
Year 10
- Transport of substances - Diffusion, osmosis, active transport, organisation.
- Digestive system - The structure and function of the human digestive system, enzymes, food tests.
- Plants - Plant tissues and organs, plant organ systems, photosynthesis, uses of glucose from photosynthesis, factors affecting photosynthesis.
- Ecology part 2 - Sampling techniques, the carbon cycle, biodiversity, waste management, land use, deforestation, global warming.
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems - The heart and blood vessels, coronary heart disease, lifestyle factors affecting health issues, aerobic and anaerobic respiration, response to exercise and metabolism.
- Structure and Bonding - Ionic, covalent and metallic bonding, giant ionic, covalent and metallic lattices - including diamond, graphite and sodium chloride. Fullerenes and graphene.
- Electrolysis - Products of molten and aqueous electrolysis, extraction of aluminium, electrolysis of sodium chloride solution, half-equations and reactions at the electrodes.
- Chemical calculations - Relative atomic and formula masses, percentage mass, chemical measurements, mole calculations, recipe calculations, percentage yield, atom economy, balancing equations.
- Energy Changes - Exothermic and endothermic reactions, reaction profiles, bond energies.
- The Earth's atmosphere - The composition of the Earth's atmosphere, carbon cycle, the Earth's early atmosphere, greenhouse gases, global climate change, human activities and their effect on the atmosphere, carbon footprint, and atmospheric pollutants.
- Particles - Density of materials, changes of state, internal energy, specific heat capacity, specific latent heat, gas pressure.
- Forces - Contact and non-contact forces, balanced and unbalanced forces, velocity and speed calculations, speed-time graphs, distance-time graphs, acceleration, Newton's Laws, Stopping distance, reaction time, momentum.
- Electricity - Circuit symbols, electrical charge and current, resistance and potential difference, resistors, Ohm's Law. Series and parallel circuits, direct and alternating potential difference, mains electricity, power and energy transfers in everyday appliances, The National Grid.
Year 11
- Homeostasis - Control of blood glucose, body temperature and water levels in humans, the human nervous system, the human endocrine system, hormones in human reproduction and contraception, the use of hormones to treat infertility, negative feedback and the roles of thyroxine and adrenaline.
- Genetics - Sexual and asexual reproduction, meiosis, DNA and the genome, genetic inheritance, inherited disorders, sex determination, selective breeding, genetic engineering.
- Evolution - The theory of evolution by natural selection, speciation, fossils, extinction, resistant bacteria, Linnaean classification.
- Variation - Genetic variation, mutations, environmental causes of variation.
- Rates - Calculating rates of reaction, factors affecting rates of reaction, catalysts, activation energy, collision theory, reversible reactions, equilibrium, Le Chatelier's Principle.
- Chemical Analysis - Formulations and pure and impure substances, testing for gases, chromatography.
- Organic Chemistry - Alkanes, fractional distillation, alkenes, cracking, combustion of hydrocarbons.
- Magnetism - Poles of a magnet, magnetic fields, electromagnetism, the motor effect, Fleming's left-hand rule and electric motors.
Geography Curriculum
Year 7
- Welcome to the World
- Map Skills
- Connectedness
- Extreme Environments
Year 8
- Water and Flooding
- The BRICs
- Climate Change
- Environmental Concerns
Year 9
- Japan
- Hazards
GCSE
Starting in the Easter term of Year 9, the Geography Department delivers the Eduqas (formerly WJEC) Specification B GCSE qualification. This is made up of three components, each of which are examined.
Component 1 is split into three cross-disciplinary themes:
- Theme 1: Changing places - changing economies
- Rural-Urban processes and change in the UK
- Urbanisation in global cities
- Development
- Theme 2: Changing environments
- Rivers
- Coasts
- Weather and climate
- Climate change
- Theme 3: Environmental challenges
- Ecosystems
- Human impact on ecosystems
- Desertification
- Water resources and management
Component 2 is problem solving geography, which is a cross-theme paper.
Component 3 is the fieldwork enquiry on which pupils are examined on their experiences of fieldwork, several of which are conducted off-site during the course.
Languages Curriculum
Year 7
- Module 1: 'Le monde et moi' (Me and the world)
- Module 2: 'Mon monde perso' (My world)
- Module 3: 'Autour de moi' (All around me)
Year 8
- Module 1: 'À table' (At the table)
- Module 2: 'Mon quartier' (My area)
- Module 3: 'Destination vacances' (Holidays)
Year 9
- Module 1: 'Le monde des médias' (The world of media)
- Module 2: 'Accro à la technologie?'' (Addicted to technology?)
- Module 3: 'Un métier, un rêve' (A job, a dream)
Years 10 & 11
- Theme 1: Identity and culture
- Unit 1: Me, my family and friends
- Unit 2: Technology in everyday life
- Unit 3: Free time activities
- Unit 4: Customs and festivals
- Theme 2: Local, national, international and global areas of interest
- Unit 5: Home, town, neighbourhood and region
- Unit 6: Social issues
- Unit 7: Global issues
- Unit 8: Travel and tourism
- Theme 3: Current and future study and employment
- Unit 9: My studies
- Unit 10: Life at school and college
- Unit 11: Education post-16
- Unit 12: Jobs, career choices and ambition
ICT Curriculum
Year 7
- Introduction to the school network - Pupils will learn about how to use school emails, FireFly, Office 365.
- E-safety - Pupils will learn about how to stay safe on-line.
- Super software skills - Pupils learn about how to use basic Microsoft packages: Excel, Word, PowerPoint and Publisher.
- Evaluation of computing - Pupils look at the history of computers.
- Introduction to programming - Pupils start to look at programming and its importance; they learn about Python.
- User Interfaces - Pupils learn about the different types of user interfaces and create a simple user interface.
Year 8
- Laws of ICT - Pupils learn about the laws that are related to ICT, e.g., The Data Protection Act, Copyright and Design Patents Act, and the Computer Misuse Act.
- Cloud Computing - Pupils understand the importance of cloud storage and cloud software.
- Programming - Pupils now develop their Python skills further.
- Spreadsheets - Pupils learn about how to create a spreadsheet model and how these can be used in real life.
Year 9
- Advance Spreadsheets - Pupils will create a spreadsheet model and use IF function, conditional formatting and pivot tables.
- Cyber Security - Pupils will look at the different types of cyber-attacks and the impacts it has on businesses/organisations.
- Project Planning Tools - Pupils will use project planning tools to create a mini project.
- Interfaces - Pupils will look at different user interfaces and understand how to evaluate them by looking at design principles.
Years 10 & 11
- Component 1 - This is an internal assessment that is worth 30%. This is a set assignment set by Pearson which needs to be completed in controlled assessment conditions. Pupils have approximately 6 weeks to complete the PSA (Pearson-Set Assignment). This unit contains 3 learning aims. For each learning aim pupils will need to complete an assignment.
- Learning Aim A - Investigate user interface design for individuals and organisations.
- Learning Aim B - Use project planning techniques to plan and design a user interface.
- Learning Aim C - Develop and review a user interface.
- Component 2 - This is an internal assessment that is worth 30%. This is a set assignment set by Pearson which needs to be completed in controlled assessment conditions. Pupils have approximately 6 weeks to complete the PSA (Pearson-Set Assignment). This unit contains 3 learning aims. For each learning aim pupils will need to complete an assignment.
- Learning Aim A - Investigate the role and impact of using data on individuals and organisations.
- Learning Aim B - Create a dashboard using data manipulation tools.
- Learning Aim C - Draw conclusions and review data presentation methods.
- Component 3 - This is an external examination that is worth 40% of pupils final marks. There are four learning aims that pupils will cover, they are:
- Learning Aim A - Modern Technologies.
- Learning Aim B - Cyber Security.
- Learning Aim C - Implications of the digital system.
- Learning Aim D - Planning and communication.
Creative Media Curriculum
Years 10 & 11
Component 1 - Exploring Media Products:
This is an internal assessment which consist of 2 learning aims. Pupils will complete 2 assignments in this component. Pupils will develop their understanding on how media products create meaning for their audience.
- Learning Aim A - Investigate media products.
- Learning Aim B - Explore how media products are created to provide meaning and engage audiences.
Component 2 - Developing Digital Media Production Skills:
This is an internal assessment which consist of 3 learning aims. Pupils will complete 3 assignments in this component. Pupils will develop their skills and techniques by reworking a media product.
- Learning Aim A - Develop media production skills and techniques.
- Learning Aim B - Apply media production skills and techniques.
- Learning Aim C - Review own progress and development of skills and practise.
Component 3 - Create a media production in Response to a brief:
This is an external assessment that is worth 40% of the final mark. Component 3 builds directly on from component 1 and 2 and enable pupils to put together everything that they have learnt into a real-life situation. In this unit there are 4 assessment objectives.
- AO1 - Understand how to develop ideas in response to a brief.
- AO2 - Develop planning materials in response to a brief.
- AO3 - Apply media production skills and techniques to the creation of a media product.
- AO4 - Create and refine a media product to meet the requirements of a brief.
Drama Curriculum
Year 7
- Base-line assessment
- Getting started on stage
- Scripts
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory
- Status and Improvisation
- Darkwood Manor
- Silent movies
Year 8
- Scripts
- Our Day out
- Pantomime
- Greek Theatre
- Shakespeare
- Matilda
- Devising
Year 9
- Scripts
- Teechers
- Theatre Practitioners
- Physical Theatre
- Soaps
- Devising
- Live Theatre review
Year 10
- Introduction to Drama
- Monologue assessment
- Theatre reviewing
- Introduction to Blood Brothers
- The roles in Theatre
- Devising skills
- Devising exam
- Preparation for Written Exam (Mock)
Year 11
- Introduction to DNA script
- Theatre reviewing
- Blood Brothers (Mock Exam)
- DNA preparation
- DNA performance
- Blood brothers and theatre reviewing
- FINAL Written examination
Music Curriculum
Year 7
- MAD T SHIRT (Elements of Music)
- Keyboard Skills (basic notation and introduction to playing the keyboard)
- Christmas Rehearsal Room (singing)
- Inspirations (keyboards)
- Get That Tune (composition)
- Sequencing (GarageBand)
- Ukulele (performance)
Year 8
- Advanced Keyboard Skills (expansion on Y7 work)
- Bhangra
- Guitar Riffs (developing skills from Y7 topic, introducing reading TAB)
- Band Project/A Cappella (performing a song on different instruments as a group)
- Film Music (GarageBand)
- Video Game Music
Year 9
- Reggae & Blues (introducing improvisation and the 12 bar blues)
- Song writing (creating all elements of a song using GarageBand)
- Advert Music (composition)
- Dance Music
- African Drumming (performance using the djembes)
- Rock Anthems (guitar)
Year 10 & 11 - OCR GCSE Music
- AoS1: My Music (2 performances and 2 compositions)
- AoS2: Concerto Through Time
- AoS3: Rhythms of the World
- AoS4: Film and Video Game Music
- AoS5: Conventions of Pop
PE Curriculum
Key Stage 3 – Years 7/8/9
In year's 7, 8 & 9 pupils have three lessons of PE per week. Please see below for the KS3 Curriculum for the year, the rotations of sports and Inter-house competitions they will be taking part in:
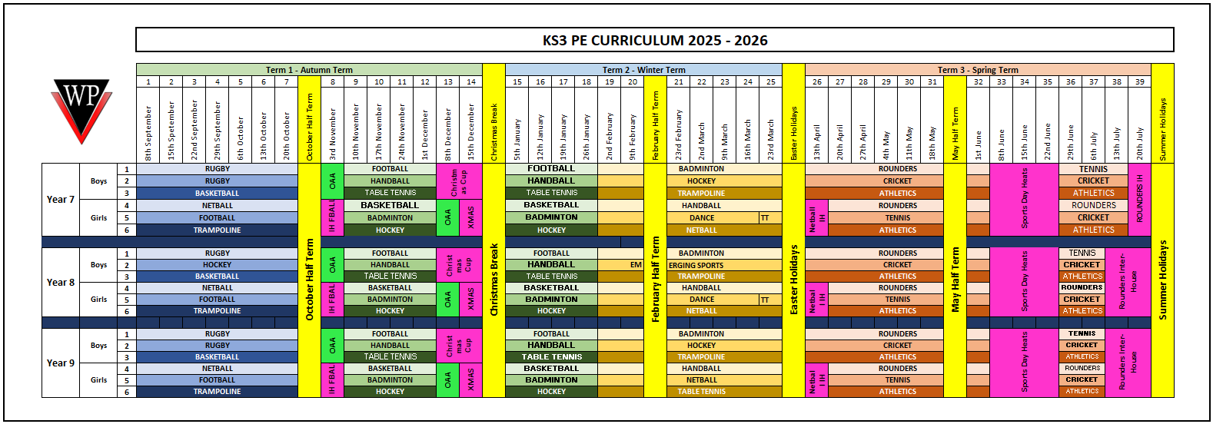
Key Stage 4 – Years 10 & 11
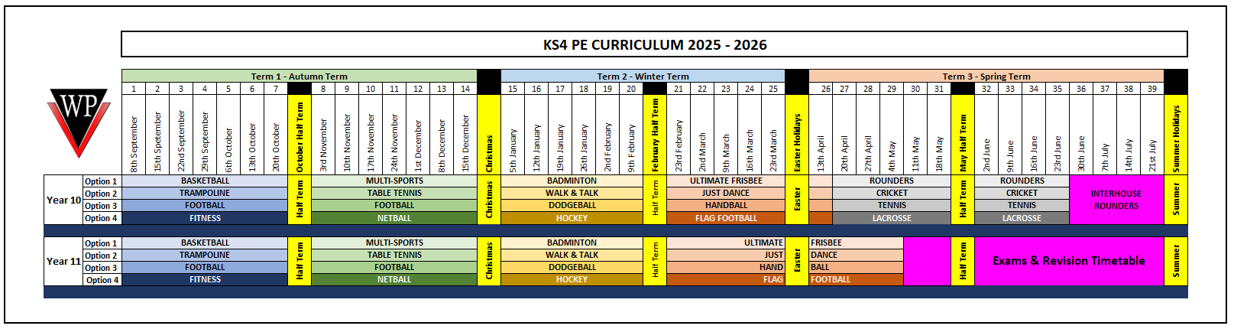
In year 10 and 11 pupils have one core Physical Education lesson per week. Pupils have the choice of the activities/sports that they study. They choose preferences towards the end of year 9 & 10 and these are catered for wherever possible within resource and staffing limitations. Please see below for the options that students can choose from:
History Curriculum
Year 7
- The Roman Empire - The origins, growth and key aspects of life within.
- Medieval England - The Norman Conquest and key aspects of life within Medieval England.
- The Arab Empire - Its origins, growth and key aspects of life within.
- Medieval Castles and Cathedrals - Key features of each with a focus on Lincoln Castle and Cathedral.
Year 8
- The Tudors and Stuarts - A study of several key monarchs and key events from within the period.
- England to Empire - The formation of the UK and the development of the British Empire.
- Slavery - British involvement in the Trans-Atlantic slave trade and key aspects of the lives of those enslaved.
- Fight for the Right - The abolition of slavery, modern day slavery and women's voting rights.
Year 9
- Industrial Britain - The key changes that took place in Britain across the Industrial Period.
- World War One - Causes and key events of World War One.
- World War Two - Causes and key events of World War Two.
GCSE
- Starting in the Easter term of Year 9, the History Department delivers the AQA GCSE qualification. This is made up of four sections, each of which are examined.
- American Expansionism 1840-1895.
- Conflict and Tension: the First World War, 1894-1918.
- Norman England c.1066-1100.
- Health and the People c.1000 to the present day.
Religious Studies Curriculum
Year 7
- Rites of Passage
- Jesus
- Judaism
Year 8
- Buddhism
- Inspiring Others
- Islam and does religion do any good?
Year 9
- Existence of God
- Christian Beliefs *
- Marriage and the family *
Year 10
- Jewish Beliefs
- Peace and Conflict
- Living the Jewish Life
- Crime and Punishment
Year 11
- Living the Christian Life
- Matters of life and Death
* All pupils begin the GCSE course of study in Year 9.
Art Curriculum
Year 7
- Fancy Footwear - Sarah Beetson/Jared Nickerson
- Drawing/Visual Elements - Klimt Leaves
- Colour Theory Painting - Klee/Sonia Delauney
- Tree of Life
- Aboriginal Art
- Classical Art
- Medieval Art - Illuminated Lettering
Year 8
- Oriental Art
- Indian Eastern Art
- Renaissance Art Caricatures
- Hands in Art - Durer/Fatima/Hamsa
- Rococco - Shells/name plaques
- Landscapes - Towers/Constable/Turner/ Hockney/Impressioninst
Year 9
- African (Picasso)
- Op Art/Pop Art - Bridget Riley / Andy Warhol / Lichtenstein
- Skulls in Art - Mexican Day of the Dead / Ed Hardy
- Street Art - Current established street artists
- Animals in Art
Year 10
- Autumn Still life - Boots/Flower or Skull/Flower.
- Landscapes - Architectural Details / Natural Elements / Holiday Views & Vistas.
- Summer Portrait - Self, Family, Friends, Pets etc.
Year 11
- GCSE Fine Art Mock Examination - One choice from selection of titles:
- Distortion
- Contrast
- Birds
- Flowers
- Doorways
- GCSE OCR Externally Set Task
D&T & Food Prep Curriculum
Within the Design & Technology and Food Preparation and Nutrition curriculum pupils experience a wide range of skills (including life skills) and gain background knowledge in preparation for their education, training and working life.
Pupils in Year 7 - 9 rotate in approximately 12 weeks blocks through the subject areas of Resistant Materials and Electronics, Graphics and Computer Aided Design [CAD] and Food and Textiles; changing classroom and teachers depending upon the module being taught.
Year 7
Resistant Materials and Electronics:
Pupils are taught basic timber and polymer knowledge through the completion of an electronic acrylic badge. They learn traditional plastic working skills by hand in the manufacture of the badge to their own design. They are also introduced to a basic LED circuit, by drilling, populating and soldering their own. Computer Aided Design [CAD] and Computer Aided Manufacture [CAM] is covered as pupils design and manufacture a sticker to go on their badge. Health and Safety in the workshop is covered at the start of the module.
Food Preperation and Nutrition:
Through a combination of practical and theory lessons, pupils learn about safe and hygienic food preparation. They will learn to safely use a range of food room equipment as well as the various parts of the cooker. Pupils will develop their knowledge of what a balanced diet is and begin to understand the functions of nutrients in our bodies. Drawing on pupil's literacy and numeracy skills they learn the importance of accurate weighing and measuring as well as converting measurements and understanding common abbreviations used in Food Preparation & Nutrition. They will learn the skills of safe chopping and preparing of fruits and vegetables as well as the rubbing in method, and simmering and boiling through their practical lessons.
Textiles:
In Year 7 textiles pupils learn about what fibres are and how they are classified into natural and synthetic. They learn that fibres are turned into yarns and fabrics by either knitting or weaving before becoming the products we use. They begin to develop an awareness of the sustainability of textiles and how we can reduce, recycle and reuse textiles. Pupils will work with knitted fabrics whilst learning how to safely use textiles equipment to include the sewing machine and irons as well as a range of decorative techniques.
Graphics and Computer Aided Design (CAD):
Pupils are taught a range of graphical techniques including a range of 3D drawing skills including; isometric, one-point perspective, and three tone rendering. Pupils complete a unit on CAD using 2D Design software where they will develop new skills and an understanding of computers in design. They will complete a mini project using their graphics skills learnt and will be introduced to Smart materials by using a thermochromic material in their mini project.
Year 8
Resistant Materials, Mechanisms and Electronics:
Pupils build upon their Year 7 knowledge by learning about timber and its working properties. They also learn about motions and mechanisms, which are closely linked with their practical project - a mechanical toy, with material finishes being introduced through the process of adding wood stain. The electronic night light project incorporates shaping acrylic using a hot wire strip heater, populating the PCB and soldering in components for pupils to create a night light. Theory behind this project includes the stages of line bending as well as identifying and understanding the electronic components.
Food Preperation and Nutrition:
Building on their experience in year 7, pupils will further their knowledge of what a balanced diet is. They will learn about the 'Eat Well' guide and have a greater understanding of how and why to reduce fat and sugar in our diets and increase the amount of fibre we eat. They will understand about safe and hygienic food preparation with a specific focus on cross contamination. They will build on their skills of melting, binding and rubbing in as well as coating through various practical dishes.
Textiles:
During Year 8 pupils will further develop their understanding of fabrics by looking at woven materials. They will broaden their knowledge of both decorative techniques and sustainability, with a specific focus on cotton usage. Pupils have the opportunity to try an advanced selection of decorative techniques whilst further developing their sewing machine skills when designing and making an organiser roll.
Graphics, Computer Aided Design (CAD) and Computer Control:
Building on techniques from Year 7, pupils further develop their graphic skills in isometric drawing and rendering with the introduction of new techniques such as two point perspective. Pupils learn about structures, how they are categorised and the forces which act upon them. They carry out a research project looking at work of others and complete a disassembly of a simple everyday object to inform their research. Pupils will learn to use Tinkercad software to introduce 3D CAD drawings, which will then be printed on the 3D printer. Pupils will also gain an understanding of computer control, where they will program a microchip with 'Inputs' and 'Outputs' to control various simulators.
Year 9
Resistant Materials and Electronics:
Pupils further build upon their knowledge of materials and CAD/CAM by design and manufacturing a light box that can be used via a USB cable. The electronic kit is populated, then soldered and located inside a timber and plywood framed box, built by the pupils to a high standard, with the front being designed to incorporate a sticker or laser cut design of the pupils choosing. Pupils also look at designing a product for a client, in readiness for GCSE. Pupils are encouraged to work more independently than in previous years, taking time to plan their work and problem solve as a team.
Food Preperation and Nutrition:
In Year 9 pupils will learn about what staple foods are and about common variations from other countries and cultures are. They will develop an understanding of the functional properties of ingredients in food. They will learn how to adapt recipes to meet the needs of different target groups such as vegetarians and diabetics. They will develop their understanding of how and why food is packaged and the use of pre-manufactured components within food production. They will build on their practical skills base with kneading and dough formation, binding and coating, batch production and a mince-based dish. A key focus of year 9 Food is to develop life skills for those who do not continue with the subject into years 10 and 11.
Textiles:
In Year 9 pupils learn about how to care for textiles, the importance of care labels and how to read them. Pupils also learn about finishes that can be applied to textiles to enhance or improve their characteristics. Pupils continue to develop their practical skills of surface decoration, use of the sewing machine and introducing them to pattern making and tie-dyeing when making a bucket hat.
Graphics and Computer Aided Design and Manifacture (CAD CAM):
In Year 9 pupils develop a greater level of skill in CAD with by using 2D Design to create a product which they will cut out on the laser cutter. Pupils carry out a research product looking into the history of a given company and their products. They will use this research to inspire designs for a piece of packaging, which will then be modelled in 3D on the computer. Pupils increase their graphic skills with a range of techniques used including: isometric, one and two point perspective, freehand sketching, orthographic and three tone rendering.
GCSE Design & Technology
Year 10:
Pupils studying GCSE Design and Technology work through a core booklet in Year 10 that covers all the knowledge that they need to know and understand on the core stand of the Specification. This includes knowledge on electronic systems, metals, paper and boards, timbers, polymers and textiles. They then study a specialist material booklet based on their chosen area of expertise; Electronics, Graphics, Resistant Materials and Textiles. Alongside these booklets, pupils have the opportunity to work through a range of mini projects as well as mini making tasks that allow them to develop their skills, knowledge and understanding of the subject area.
Year 11:
The primarily task for pupils during Year 11 is the completion of their Non-Exam Assessment, which is worth 50% of their GCSE. This is started at the end of Year 10 and combines a pupils experiences with the focus of designing a product to meet the need of a client. Pupils work through the creation of an innovative design folder that helps address an area of topic provided by the exam board - AQA. Once this work has been produced, the remaining time is spent revising their knowledge in readiness for the summer examination; worth the final 50% of a pupil's grade.
GCSE Food Preparation and Nutrition:
Year 10:
During year 10 pupils will develop a knowledge and understanding of the 5 keys topics; Food Nutrition & Health, Food Science, Food Safety, Food Provenance and Food Choice. They will do this through a combination of theory, practical lessons and practical investigations. Pupils will build on skills learnt in years7, 8 & 9 and learn knife skills such as; vegetable preparation like julienne, baton and dice as well as meat preparation such as joining a chicken. Pupils will develop a large repertoire of practical skills to include sauce making, and dough formation in the form of bread and pasta amongst others.
Year 11:
Pupils will use the knowledge and skills they have developed in Year 10 to answer 2 Non-Examined Assessment (NEA) tasks assigned by the examination board. The first is an Investigation task where pupils research the functional and chemical properties of ingredients and present their findings in a report. The second is a food preparation task where pupils are to plan, prepare, cook and present three dishes to meet with a target group and/or nutritional focus. In this project pupils will have the opportunity to showcase the variety of technical skills they have developed during the course in. Year 11 will culminate in a written examination to test the theory knowledge acquired throughout the course.
Personal Development Curriculum
Personal Development at West Park School covers both statutory content for PSHE (Personal, Social, Health and Economics) and Careers. Please find below some FAQs regarding the PSHE Curriculum:
What aspects of PSHE are now compulsory under government guidance?
Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) aspects of PSHE education will be compulsory in all schools as of 2020. In PSHE we also teach students about Health and Wellbeing (including physical and mental health) and Living in the Wider World (including careers and money management).
What topics are covered in RSE at West Park School?
RSE lessons cover a range of topics including; Healthy relationships, including friendships and intimate relationships; families; growing and changing, including puberty; personal hygiene; changing feelings; becoming more independent; keeping safe and consent. Pupils will also have opportunities to ask questions that help prepare them for relationships of all kinds in the modern world.
What are the rules on the Right to Withdraw from Relationships and Sex Education (RSE)?
Parents have a right to request to withdraw their child from sex education delivered as part of RSE in secondary schools which, unless there are exceptional circumstances, should be granted up to three terms before their child turns 16. At this point, if the child themselves wishes to receive sex education rather than be withdrawn, the school should make arrangements for this to happen in one of the three terms before the child turns 16 - the legal age of sexual consent.
You can view the current Personal Development Curriculum by clicking here.
How do I talk to my child about the time they spend online and social media usage?
Talking to young people about technology and social media can be difficult when we dont use the same platforms or watch the same content. For further information on how to safeguard your child online use the link below to the website Internet Matters: Keep Children Safe Online: Information, Advice, Support - Internet Matters. This information on how to set up devices safely and choose age appropriate apps.
There are also tips on how to tackle online issues with your child. See link on information about online misogyny as an example: What is misogyny? Guidance for parents and carers| Internet Matters
